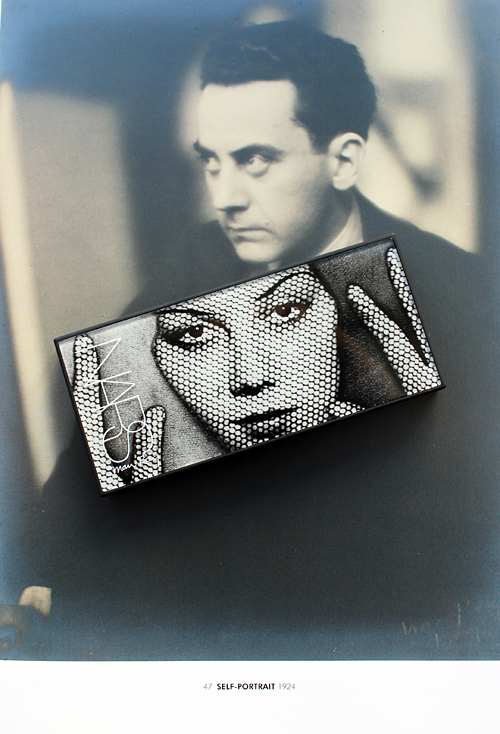
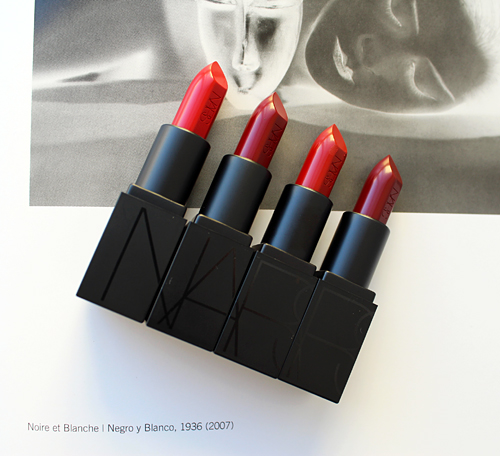
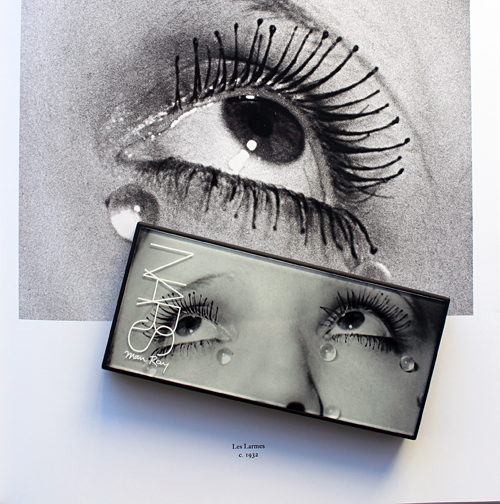
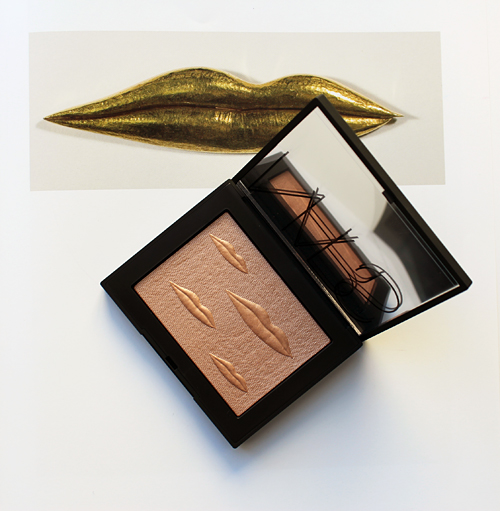
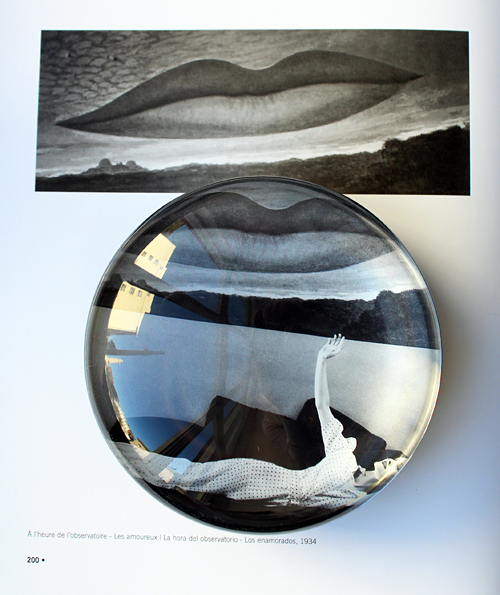
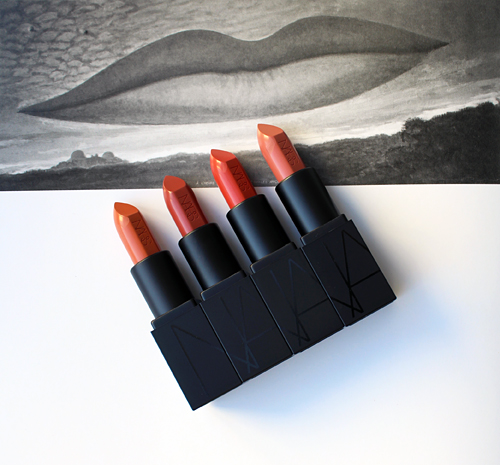
The general process for this post was to try to write something, immediately get overwhelmed and move on to something else. Hence why it took me 5 years to come up with anything on NARS's holiday 2017 collection, which featured the work of Surrealist artist Man Ray. November 18, 2022 marks the 46th anniversary of the artist's passing, and since NARS's recent collections have been very lackluster I thought this is finally the year I get a post up about the Man Ray collab.
Fortunately (or unfortunately) there is a ton of information about the collection and Man Ray's work. I'm not going to delve too much into it because there are literally entire books on Man Ray, but I will highlight the artwork used in the NARS collection and the process behind it, along with some other connections between Man Ray and makeup outside of the collaboration. As with Sarah Moon and Andy Warhol, Francois Nars chose an artist that has inspired him for years. "You know it’s almost always the same the process [with these collaborations]. They’re always with people that inspire me either since I was a kid or for many, many years. I really pick them randomly, it’s pure attraction. I just think, 'Why don’t we do a collaboration with Man Ray?' It’s really people that have been influencing me a lot in my work, in my photography, in whatever I do. And people who I really love what they do. It’s very pure and simple." He approached the Man Ray Trust about using the artist's work for a makeup line, and was thrilled when they agreed.
Nars discovered the work of Man Ray as a teenager. The modernity of Man Ray's oeuvre as well as the range of subjects he captured for his portraits immediately caught Nars' eye. "I read that every time Man Ray received a visitor in his studio, he'd photograph them," he explains. "He couldn't help it. It could be a friend, his lover, the postman, his housekeeper. He loved taking photographs of anyone he ever met, which is something I can relate to. He was a great inspiration for me when I was starting out as a photographer…I always loved his portraits. That was something I kept in mind. My photography background influence is quite wide, but he had a very distinctive eye on photography and the way you photograph people. The lighting, the abstract feeling in his photographs, sometimes it became more like a painting—there was so much poetry. The poetic aspect in his photos is so interesting." Nars, a self-declared rule-breaker when it comes to makeup, also admires Man Ray's selection of unusual models, favoring those who did not possess conventional beauty but who were remarkable in their own way. "[I] remember the women in Man Ray's photographs were so dramatic in their looks and their choice of make-up. Man Ray was very daring in his casting, he was always searching for that type of unique beauty. I can relate to that, I don't tend to go for simple, pretty faces."
The use of makeup in Man Ray's photos strengthened their compositions despite (or maybe even due to) the absence of color. Nars points out that the makeup in Man Ray's work encourages the viewer to consider shadows, angles, contrast and the overall significance of the image rather than being distracted by vivid hues. The same principles can be applied to the face, i.e. color is not necessarily required to make an impact when the focus is on texture, placement, shapes, etc. "To me, something brilliantly coloured can look great represented in black and white. The lack of colour forces you to see something deeper in the object, but often just as beautiful. Make-up is similar. It’s not always about colour on the face. A very graphic, lined eye or defined lip creates a look that isn’t about colour at all. And, of course, some make-up – black eyeliner or a very dark red lip against pale skin – can appear almost black and white…As a make-up artist, I studied Man Ray’s models very carefully: the shape of a lip, the graphic eyeliner, the placement of the rouge on the cheek. The incredible thing about Man Ray is how his style still seems new, fresh, sharp, even today."
Dr. Wendy Grossman, an art historian and Man Ray expert who advised Nars on the collection, echoes his sentiments. She says, "Man Ray himself paid close attention to the way in which his models were made up. His radical cropping aesthetic led to dramatic images of lips, eyes, and hands, all of which draw the viewer’s attention to the components of the body most enhanced through the use of makeup. Man Ray was very precise and involved with the way his models were made up and staged for his photographs. Man Ray’s special talent was to bring out the unique beauty in each of them and find ways to add a 'surreal appeal' in the way he used lighting, shadows, camera angles to infuse his compositions with mystery and intrigue."
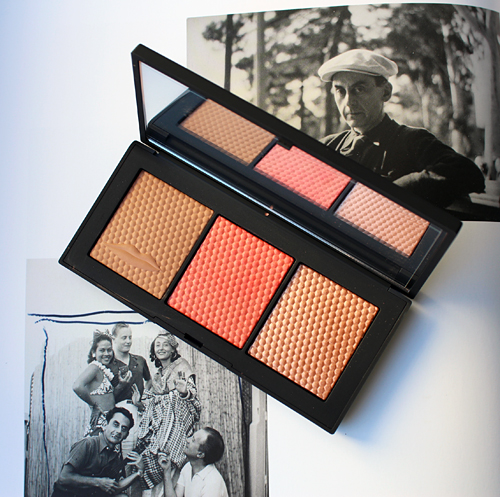
Indeed, Nars himself notes that trying the process of figuring out appropriate colors for the collection was an enjoyable one. "For me, part of the fun of looking at old black and white photographs is imagining what makeup colours and textures were used. Of course the models are wearing colour-probably black eyeliner, powder, dark lip colour-only we can't see it. I also like to imagine what colours Man Ray might have been drawn to if he was working today. And, almost as important, is the aesthetic and vision of beauty that Man Ray represented – it is bold and moody, and a little irreverent and edgy. That's what we have tried to capture in the shades of this collection." However, various shades of red as seen in the set below don't seem that daring; a deep eggplant shade or even black may have been more adventurous and representative of Man Ray's spirit.
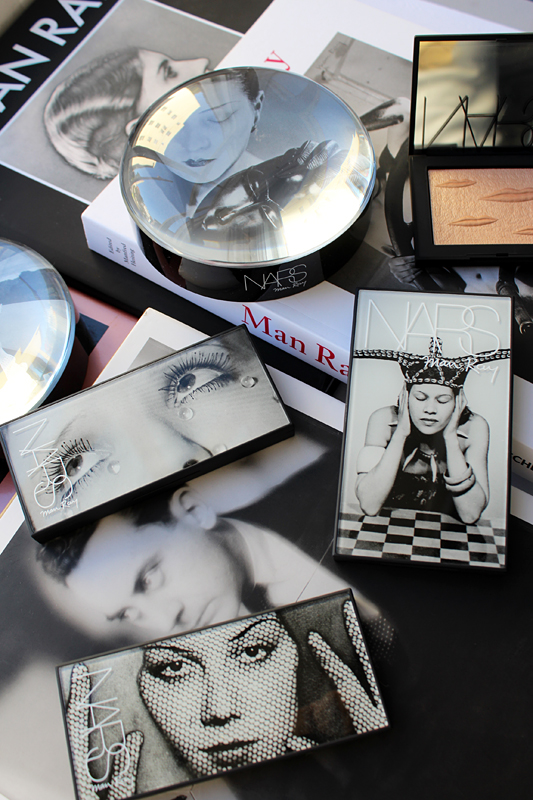
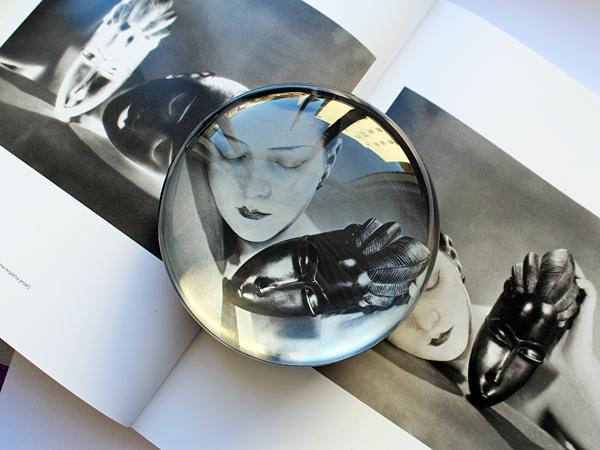
Nars states his choice of Man Ray images for the collection were driven by "pure instinct, love and attraction." He was drawn to Man Ray's still life photos, but ultimately ended up selecting those that emphasized the face or certain body parts since they were more relevant to makeup. He also wanted to include Man Ray's most famous and iconic works, such as 1932's Glass Tears: "[While] many people might recognize the image, they may not know that it was Man Ray who created it, and also because as beauty images go, it's perfection." Appropriately enough, Glass Tears was used for a mascara ad.
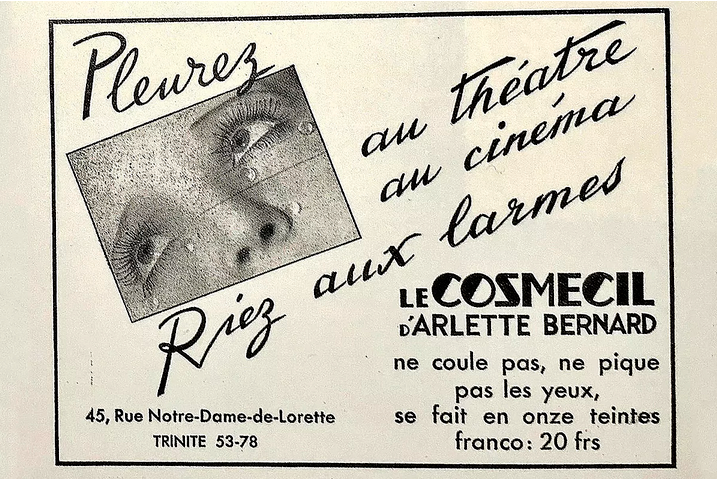
(image from elmundo.es)
The gold lip motif throughout the collection packaging was devised by longtime NARS art director Fabien Barron and a reference to the golden sculpture of the lips of his former lover Lee Miller.
Dr. Grossman explains how Man Ray became preoccupied with Miller's lips and how he incorporated them into much of his work after their split in 1932. "The lip motif began with Lee Miller, Man Ray’s model, muse and lover from 1929 to 1932. She had beautiful lips, which were featured in many of his photographs. She left him after a tumultuous affair, and he expressed his anger and hurt through an obsessive focus on her lips."
One of Man Ray's most famous images besides Glass Tears, The Lovers: Observatory Time (1936) was also used to sell makeup. It was exhibited at the end of 1936 in MoMA's "Fantastic Art, Dada, Surrealism" show. When the show closed the artist received a telegram from Helena Rubinstein requesting the painting. Man Ray states in his autobiography that he was "overjoyed" to let Madame borrow it for one of her stores in Manhattan. "[With] this windfall I’d be able to devote more time to painting in the future. After awhile, the painting carefully crated was returned to me followed by a letter of thanks from Madame Rubinstein. She had displayed it in her magnificent new beauty emporium on Fifth Avenue, featuring a new lipstick or some other beauty product. This I was told by some outraged friends. However, I wasn’t too upset; I was glad to have the painting back and showed it again in the Paris Surrealist show the next year."1
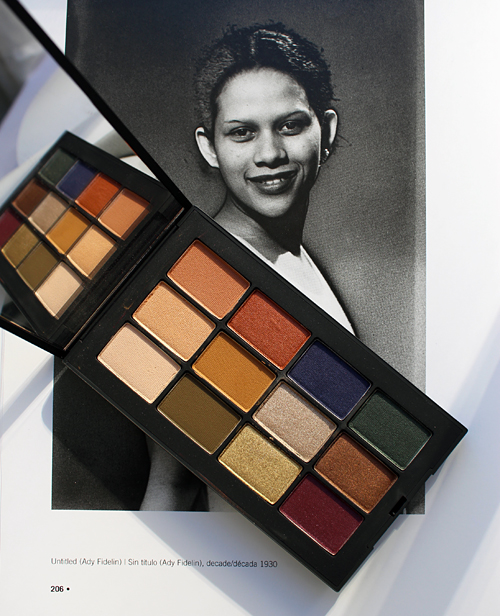
One of the more intriguing images chosen by Nars for the collection was a photo of his muse and model Adrienne "Ady" Fidelin. Ady was a dancer from Guadalupe and became the subject of nearly 400 of Man Ray's photos after they met in 1936. Dr. Grossman, whose upcoming book "Seeing 'Ady': Adrienne Fidelin, Man Ray, and the Recovery of a Black Surrealist Muse," presents an in-depth look at Ady and her relationship with the artist. She notes, "As with Man Ray’s other muses, Adrienne inspired him to create innovative images that drew on her engaging personality and unique attractive qualities. He found cause on more than one occasion to use her 'café au lait' skin tone as a compositional feature to play on the theme of black and white that permeated his photographic work."
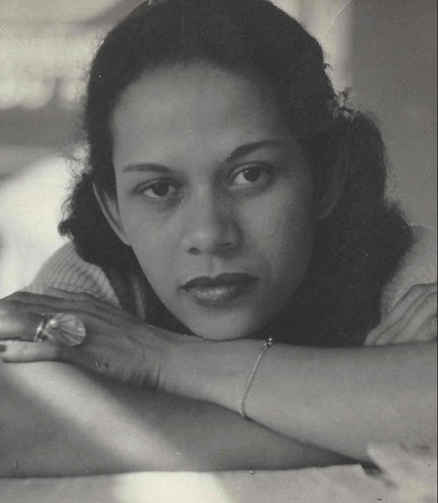

(image from mubi.com)
The image that appears on the eyeshadow palette originally appeared in the September 15, 1937 issue of Harper's Bazaar. It was part of a larger collection of roughly 30 photos entitled "Mode au Congo" in which models wore an array of Congolese headdresses borrowed from a Paris gallery. In "Unmasking Adrienne Fidelin: Picasso, Man Ray, and the (In)Visibility of Racial Difference," Dr. Grossman explains the significance of Ady's Harper's Bazaar portrait. She points out that in a strange paradox, the exotification and racialization of Ady permitted her to be the first Black model in a leading American fashion publication. "The only model of color among those the artist posed sporting one of these headdresses, Fidelin is represented in all nine compositions in which she features in a manner that draws attention to her racial difference: bare shouldered (and bare breasted in several), outfitted with a tiger’s tooth necklace and ivory bangle, and seductively posed…This treatment is exploited in a spread in the September 15, 1937 issue of Harper’s Bazaar where selected images from this series frame an essay by the French surrealist poet Paul Éluard. In the full-page reproduction taking up one half of the spread, the Guadeloupean model is staged to evoke the fashionable 'African native' extoled in the article’s headline, 'The Bushongo of Africa sends his hats to Paris.' This fanciful projection of difference and the assimilation of Fidelin’s identity into a homogenizing notion of blackness literally and figuratively sets her apart from the white European models similarly crowned in Man Ray’s [other] photographs…Ironically, it is arguably this paradoxical treatment of Fidelin that led to the publication of the image even in the face of intransigent racial barriers in the fashion industry. This Guadeloupean woman in the guise of an African thus unceremoniously became the first black model to be featured on the pages of a major American fashion magazine." On the one hand, Nars' inclusion of Ady can be viewed as positive, since even former art history majors and Surrealism enthusiasts such as myself were not aware of her or the fact that she broke significant ground in the fashion world. On the other hand, it may have been more appropriate to use a less exotified image of Ady, iconic though it may be. Plus, if it was really an inclusive gesture meant to familiarize the public with Ady, the company would not have made the decision to sell the palette in a very limited market – to my knowledge, Love Game was only available in the U.K.
In any case, another interesting cosmetics connection to consider is that Man Ray himself dabbled in makeup, frequently painting the face of Kiki de Montparnasse, his lover from 1921-1929. According to biographer Neil Baldwin, "[Man Ray] designed Kiki’s face and painted on it with his own hand. First Man Ray shaved her eyebrows completely, and then he applied others in their place, varying the color, thickness, and angle according to his mood. Her heavy eyelids, next, might be done in copper one day and royal blue another, or else in silver or jade."2 Scholar Susan Keller notes that by applying her makeup in this way, Man Ray was helping to develop a public persona for Kiki rather than portraying a likeness of her. "Instead of representing her, Man Ray was producing her, creating a public mask that was impossible to view separate from her, unlike a portrait on canvas, where the original and the copy (the woman and the portrait) are easily distinguished."3
Man Ray also applied Kiki's eye makeup for his short 1926 film Emak Batia. The artist explains: "[Kiki's] penchant for excessive makeup gave me the idea. On her closed eyelids I painted a pair of artificial eyes which I filmed, having her open her own eyes, gradually disclosing them. Her lips broke into a smile showing her even teeth. Finis – I added in dissolving letters."4
Keller explains how Man Ray elevated makeup to a true art form. "[Man Ray’s] cosmetic games were hardly unique; countless women have used and still do use makeup to reinvent or to stabilize their appearances every day. Man Ray’s status as an artist, however, and his Surreal play with the conventions of makeup, serve to expose by making marvelous women's everyday behavior usually seen as too trivial or mundane to be contemplated in any depth…In keeping with the Surrealist themes of dreams and the unconscious, Kiki’s fantastic makeup shows her both literally awakening and what might be seen as a metaphoric awakening from the deadening world of everyday assumptions, moving from the world of the real to the more-than-real or surreal, just as the film itself was supposed to shock audiences out of their mundane lives into a receptivity for more utopian possibilities."5 This makes sense; however, I still think the idea of makeup as art in this case would not have happened if a Surrealist woman artist, such as Méret Oppenheim or Leonora Carrington, had painted Kiki for the film. The popular perception at the time was that makeup is art only if a man does it. It's akin to food preparation in that women are cooks but men are chefs.
As with all artist collabs, there was speculation about what Man Ray would have thought of his work appearing on a makeup collection. Personally I agree with Dr. Grossman that he would have been flattered, especially given his positive endorsement of Helena Rubinstein putting his art in a store window. "I think Man Ray would appreciate seeing his photographs embraced in this fashion. It would probably not surprise him that the invitation came from a Frenchman; he always felt that the French had a much greater appreciation of his vision and creative practice than did people in his native United States."
Now for a special treat. Via one of the Museum's board members, I had the incredible honor of talking with Dr. Grossman herself about this collection! She was also kind enough to share a photo of the PR box she received from NARS. Truly museum-worthy!
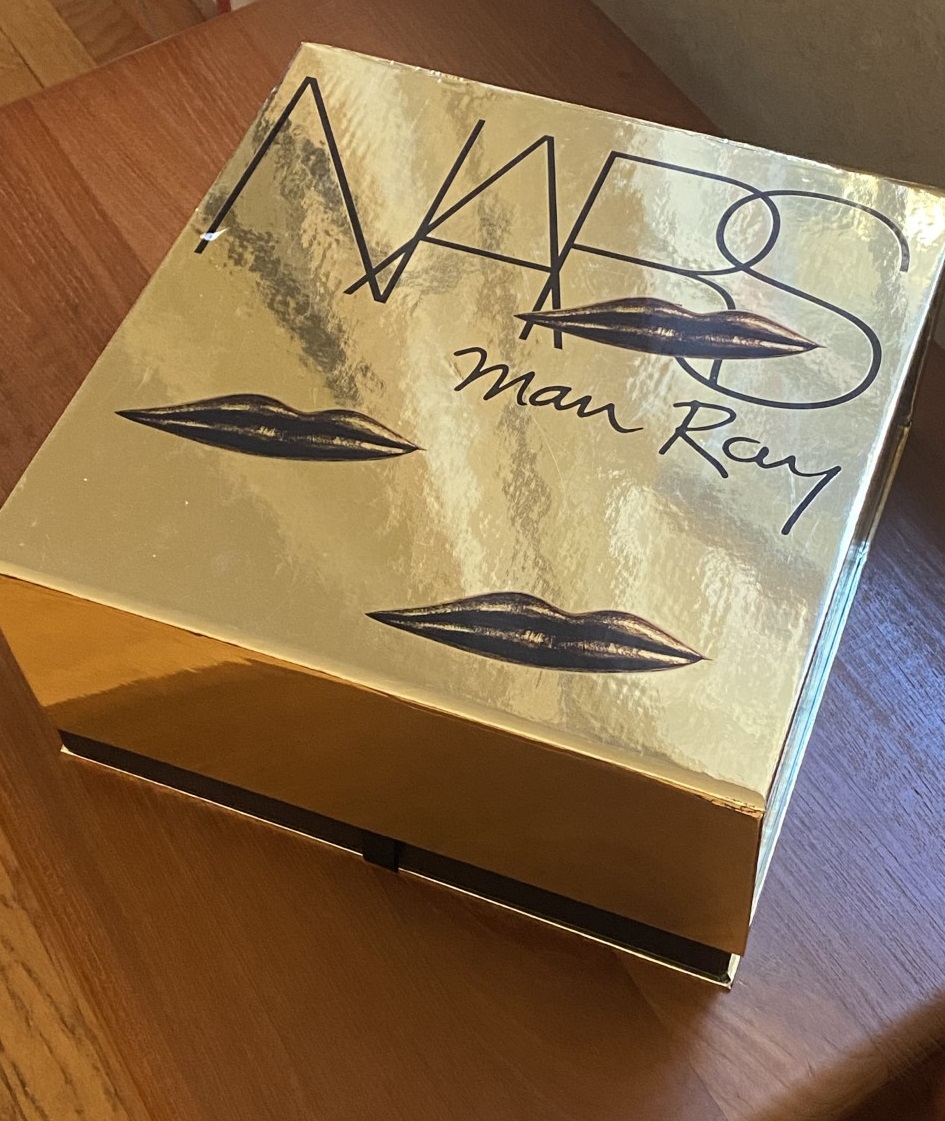

(image courtesy of Dr. Wendy Grossman)
What do you think of this collab and Man Ray? Would you like to see a deep dive into Surrealism and makeup?
1Man Ray, Self-Portrait (Boston: Little, Brown and Company, 1963), 257-258. For more on Rubinstein's usage of Man Ray's work, see Marie Clifford, "Brand Name Modernism: Helena Rubinstein’s Art Collection, Femininity, and the Marketing of Modern Style, 1925-1940," (PhD diss. University of California, Los Angeles, 1999).
2Neil Baldwin, Man Ray, American Artist (New York: C.N. Potter, 1988), 107.
3Susan Lynn Keller, "Making Up Modernity: Fashioning the Feminine in Early -Twentieth -Century U.S. Culture" (PhD diss., University of California, Santa Barbara, 2008), 238, ProQuest (3330475). By contrast, Lee Miller did not allow Man Ray to "create" her by allowing him to apply makeup: "Some said that Man had 'created' Kiki by designing bizarre makeup and painting it on her – even shaving off her eyebrows and replacing them with new ones at odd angles. Lee needed no embellishment, nor would she submit to being redesigned." From Lee Miller: A Life by Carolyn Burke, (New York: Knopf, 2005), 81.
4Man Ray, 272.
5Keller, 238.















