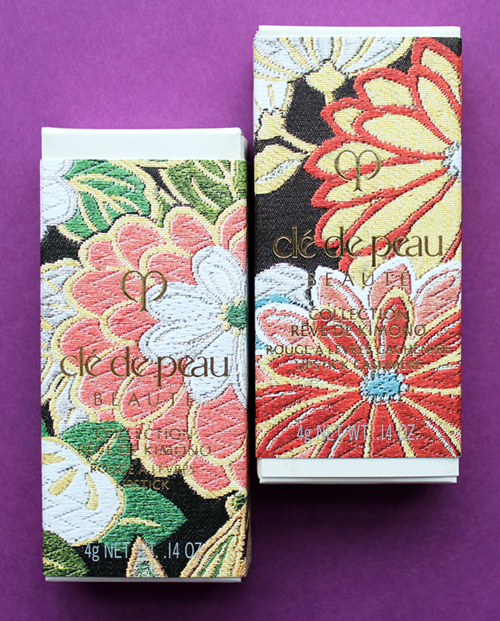
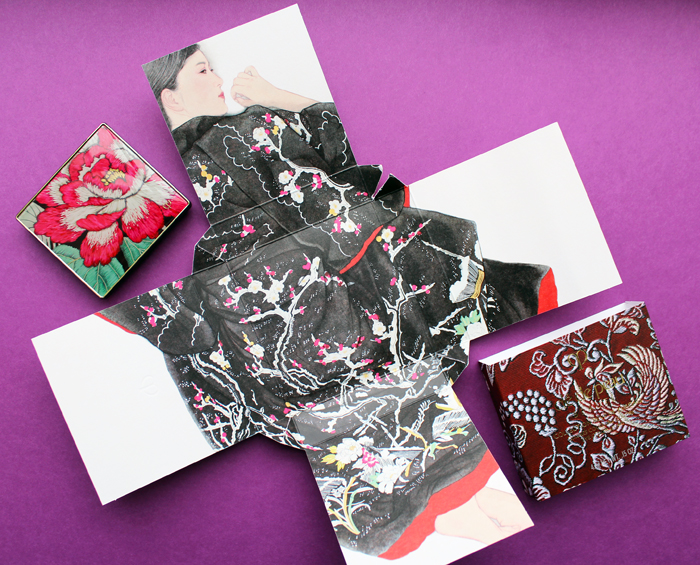
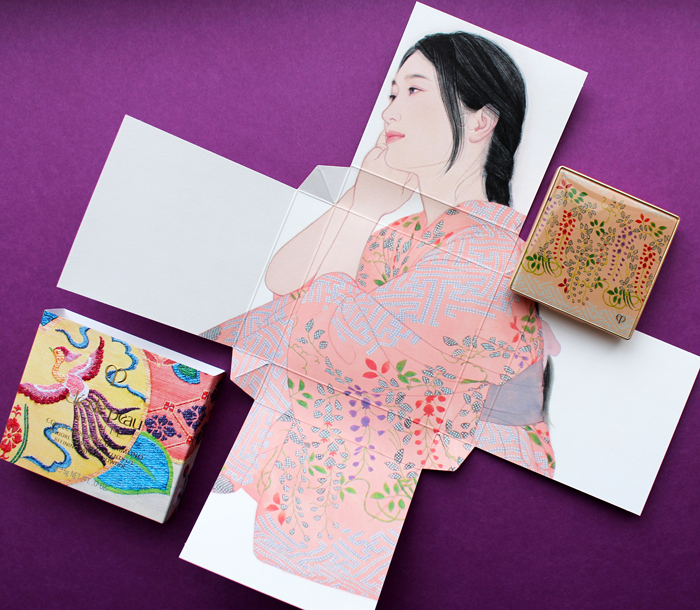
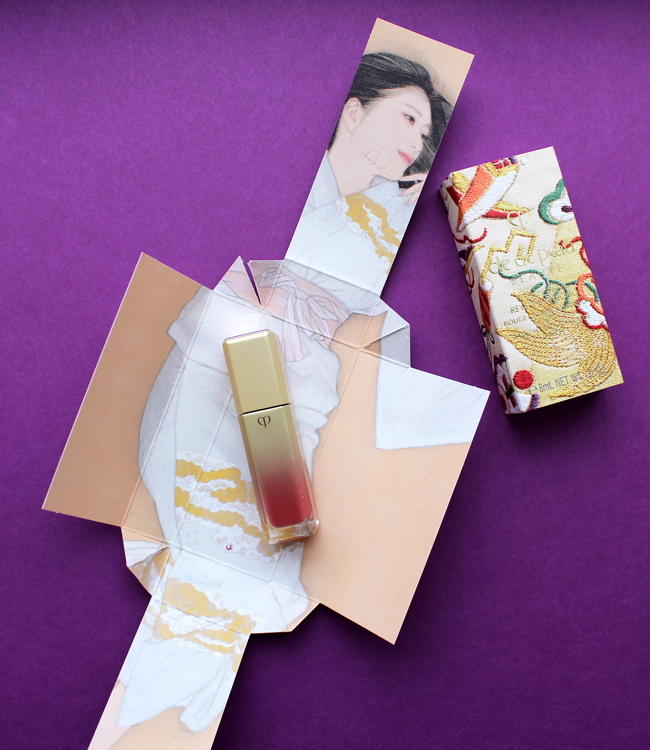
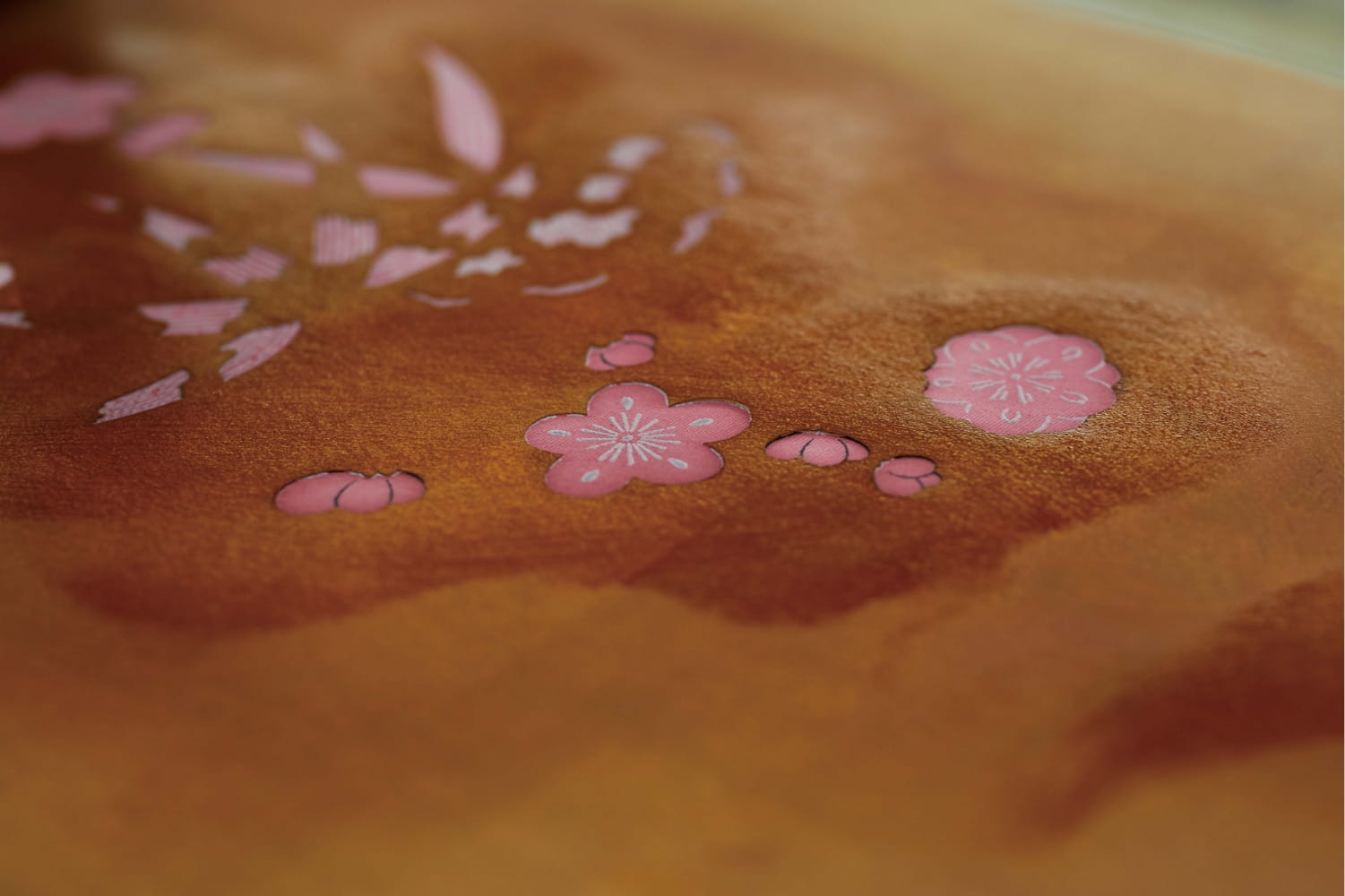
Clé de Peau continues their streak of beautiful and inspired holiday collections. This year's theme, Kimono Dream, is an homage to two venerable Japanese art forms: the kimono and bijin-ga ("pictures of beautiful women"). Obviously a deep dive into the history of both of these is way beyond this blog post, but as usual I'll provide a condensed version. First, let's take a look at the collection itself.
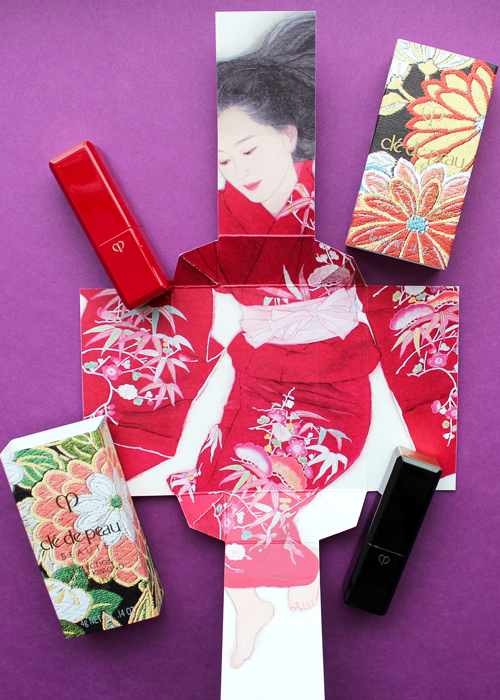
Each piece is packaged in a sturdy paper sleeve. Remove the sleeve, and the package opens to reveal a bijin-ga painting featuring a woman wearing a kimono. The intricate folding is reminiscent of how the traditional kimono is held in place with an obi, the decorative sash worn around the waist, as well as tatou, the folded paper used to wrap and store silk kimonos to protect them from humidity. The patterns on the sleeves are inspired by obi patterns as well. The unfolding aspect of the packaging is gorgeous and highlights traditional Japanese art, but it's also perfect for the theme Clé de Peau wanted to express, which was revealing women's inner beauty. Each painting represents one of four traits: passion, strength, charm and gentleness.
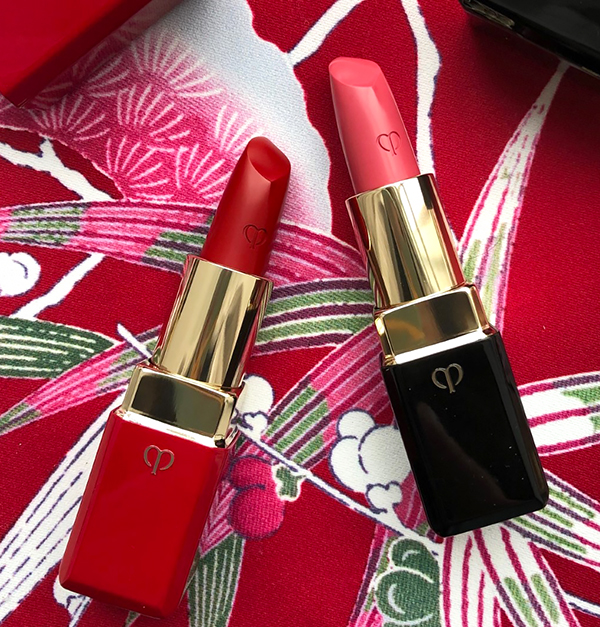
It's a bit contrived, but I appreciate that Clé de Peau took the time to align the products with the traits they wanted to convey and write little descriptions for each. Here's the one for the lipsticks, which symbolize passion. "Intense. Dynamic. Instantly revealing the passion within. Represented by plum, and evergreens pine and bamboo, against bright red silk. Despite your elegant façade, the force of your passion is unmistakable. A signal of powerful emotion that can’t be concealed."
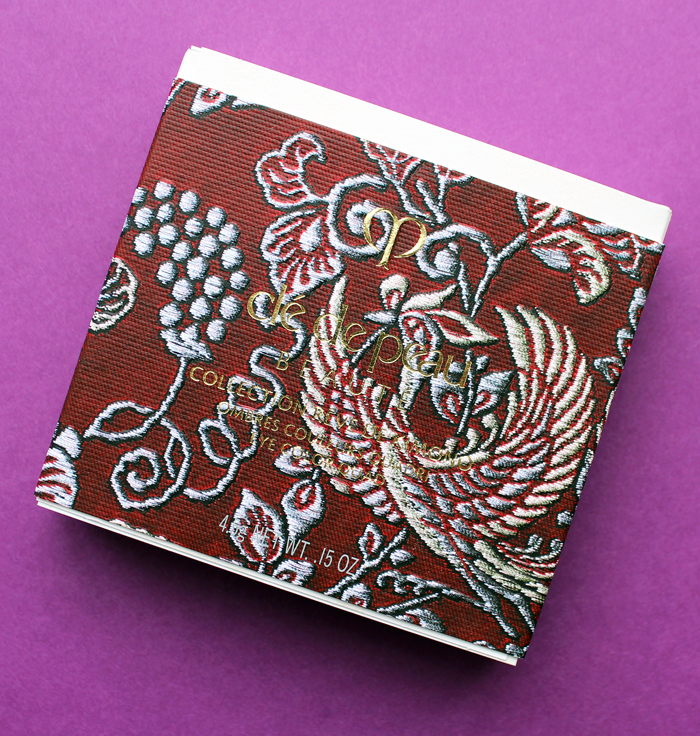
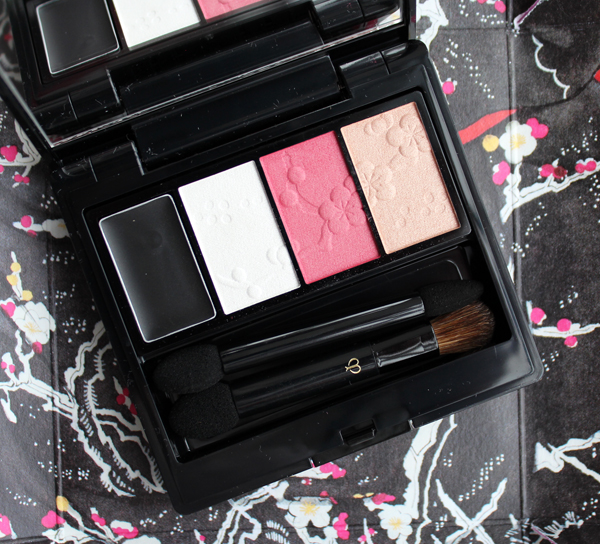
The eyeshadow quad was my favorite piece – I loved the striking black kimono shown on the woman contrasted with the delicate embossing on the shadows. "Strong, essential, with a flash of feminine red. Peonies and daffodils bloom in the snow, showing determination and vitality. A woman at one with her inner strength. Noble, dignified, the plum tree signifies resilience. You look outward at the world, through confident eyes."
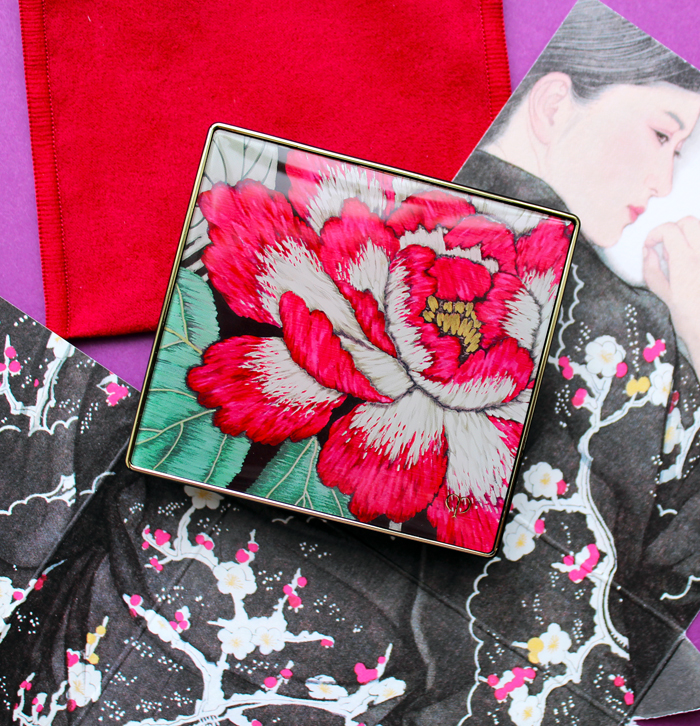
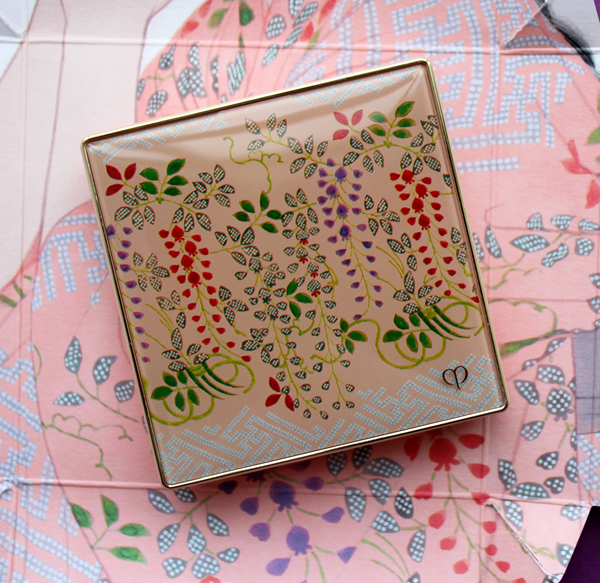
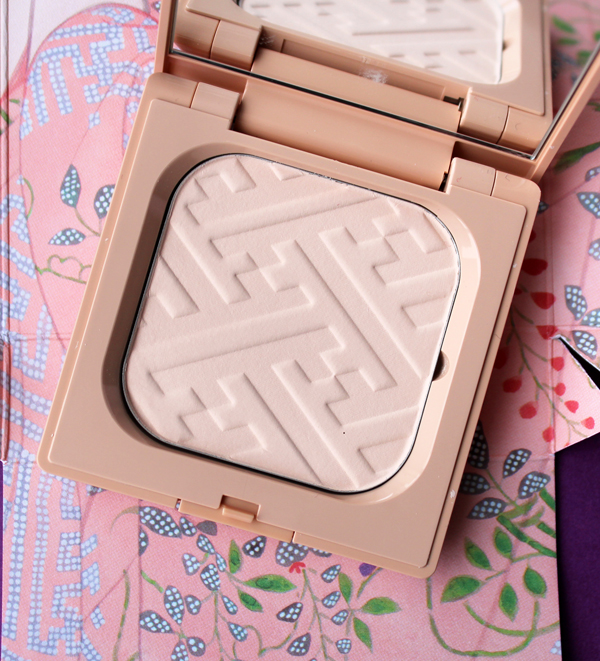
Next is the face powder, signifying charm. "Evoking prettiness and innocence. Symbolized by the peacefulness of wisteria and chrysanthemum against soft salmon-pink. Inspired by the simplicity of flowers, you rest sweetly in softness."
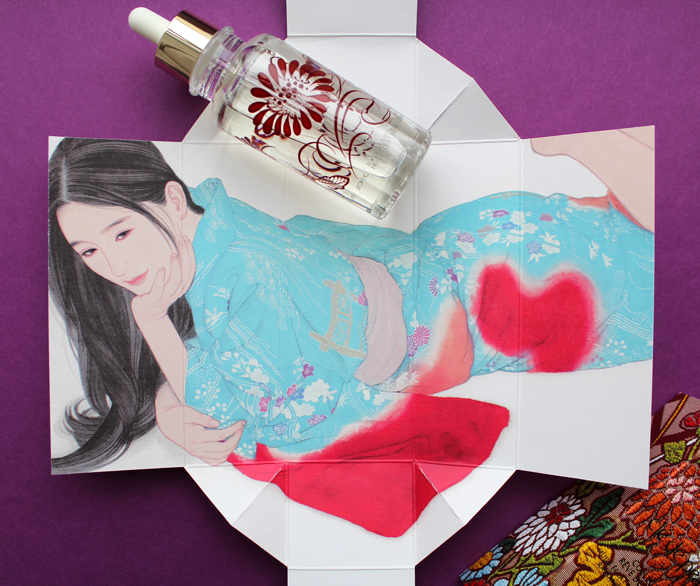
Finally we have the face oil, which embodies gentleness. "Your open, unbounded heart. Fresh blue silk accented with vermillion and soft pink. The serenity of a goldfish in water. Cooling, refreshing, harmonious. Surrounded by gentleness, you are wholly embraced."
There was also a matte liquid lip color, but that didn't seem to be included in the four traits. Nevertheless it is stunning and the packaging was different than the others so I had to include it!
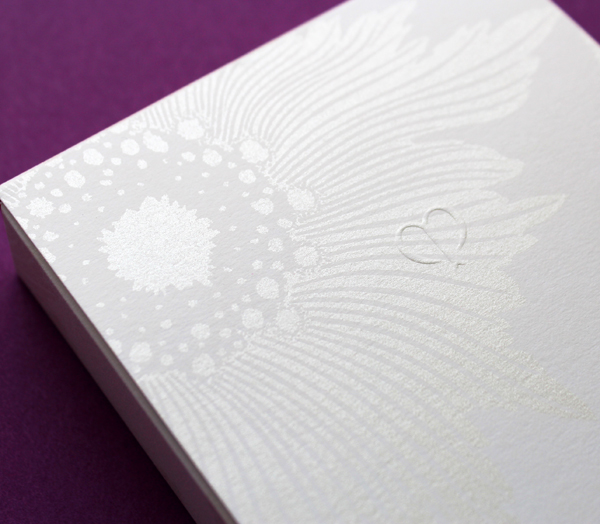
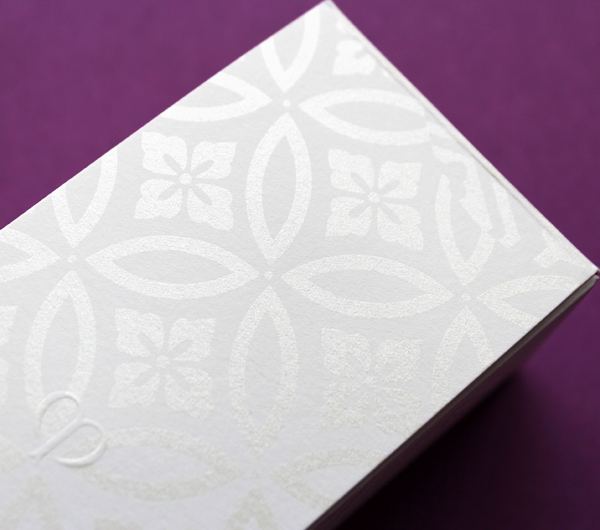
I couldn't resist sharing the embossing on the outer boxes. Such a nice little touch.
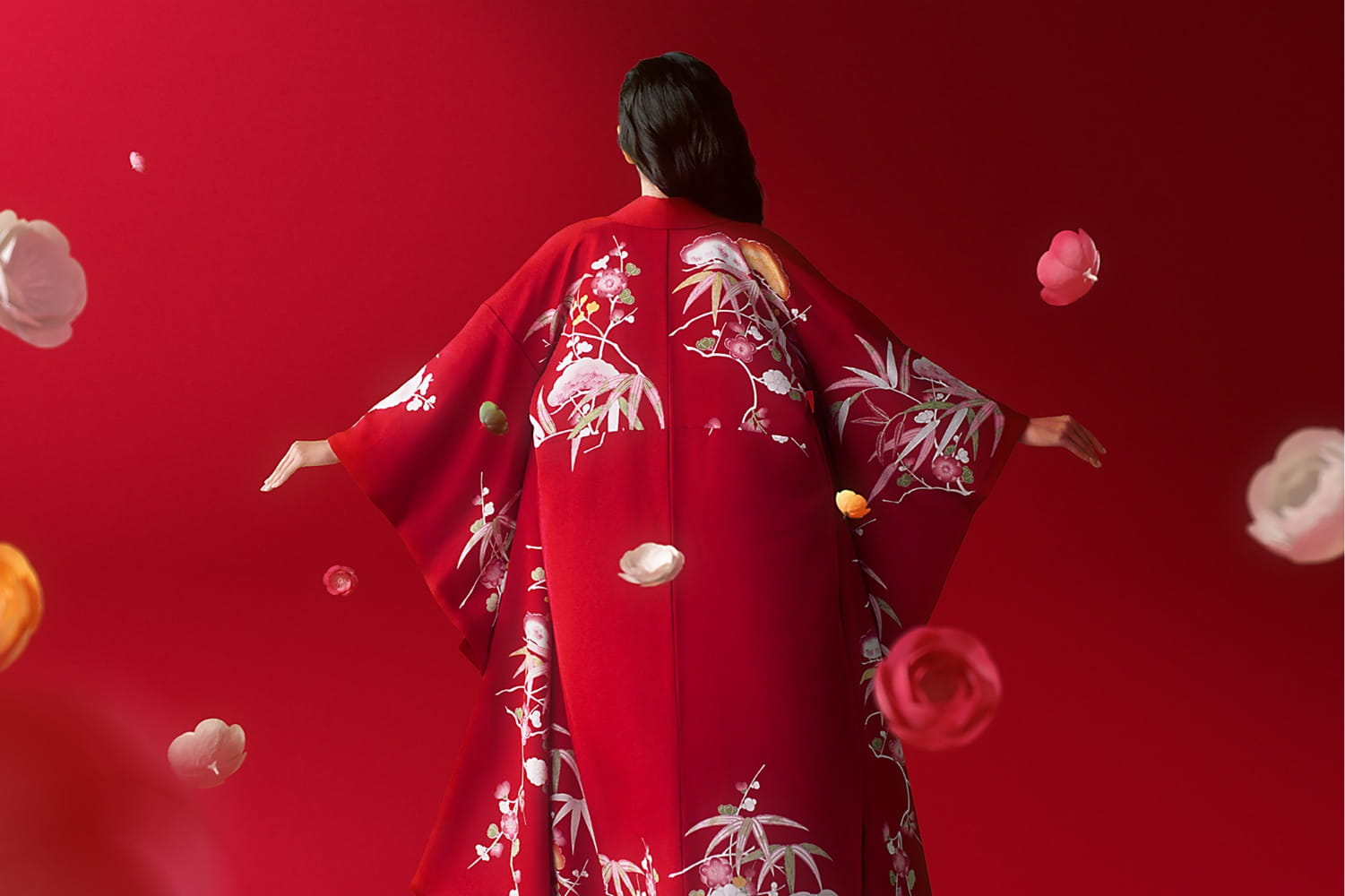
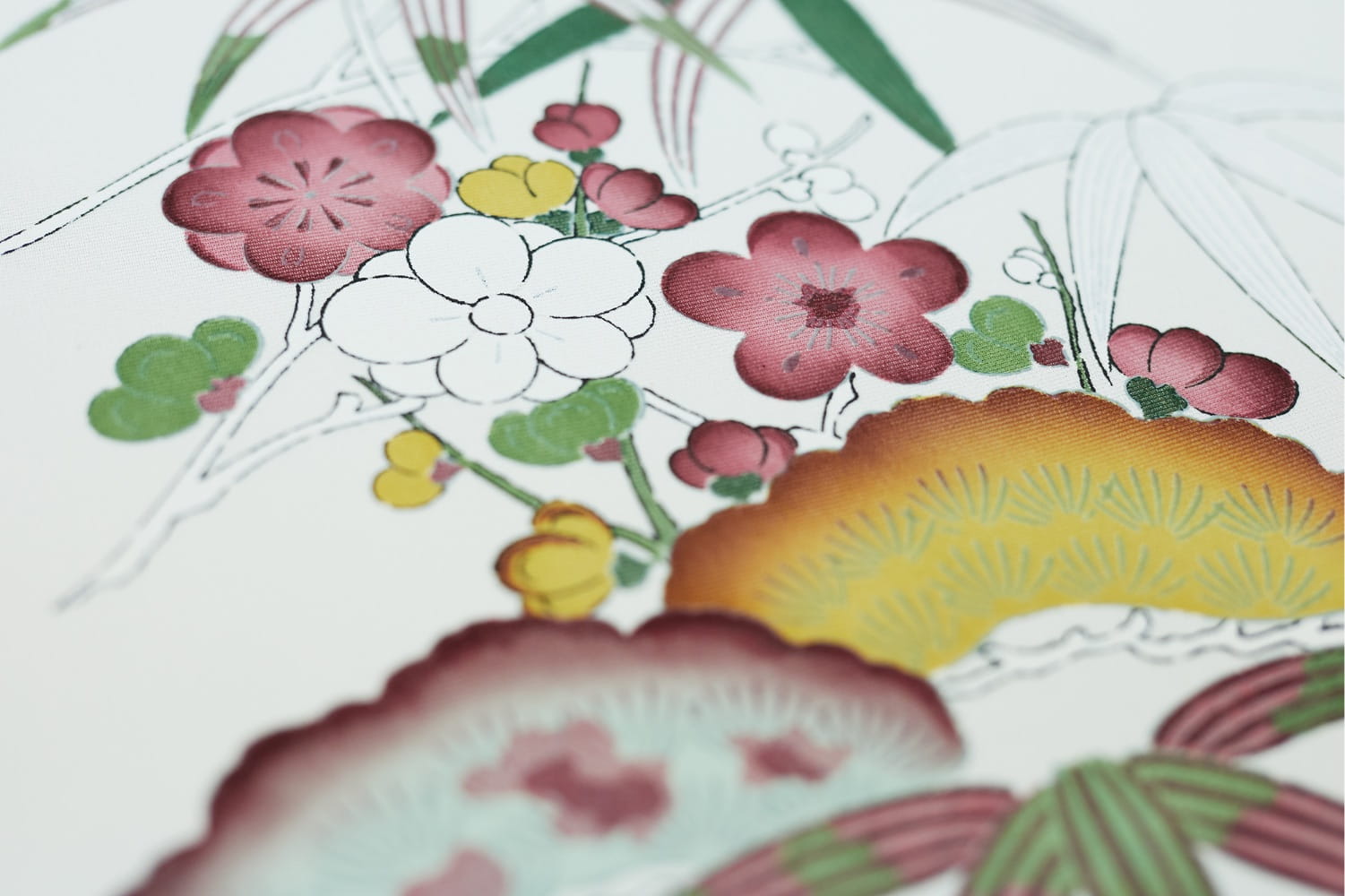
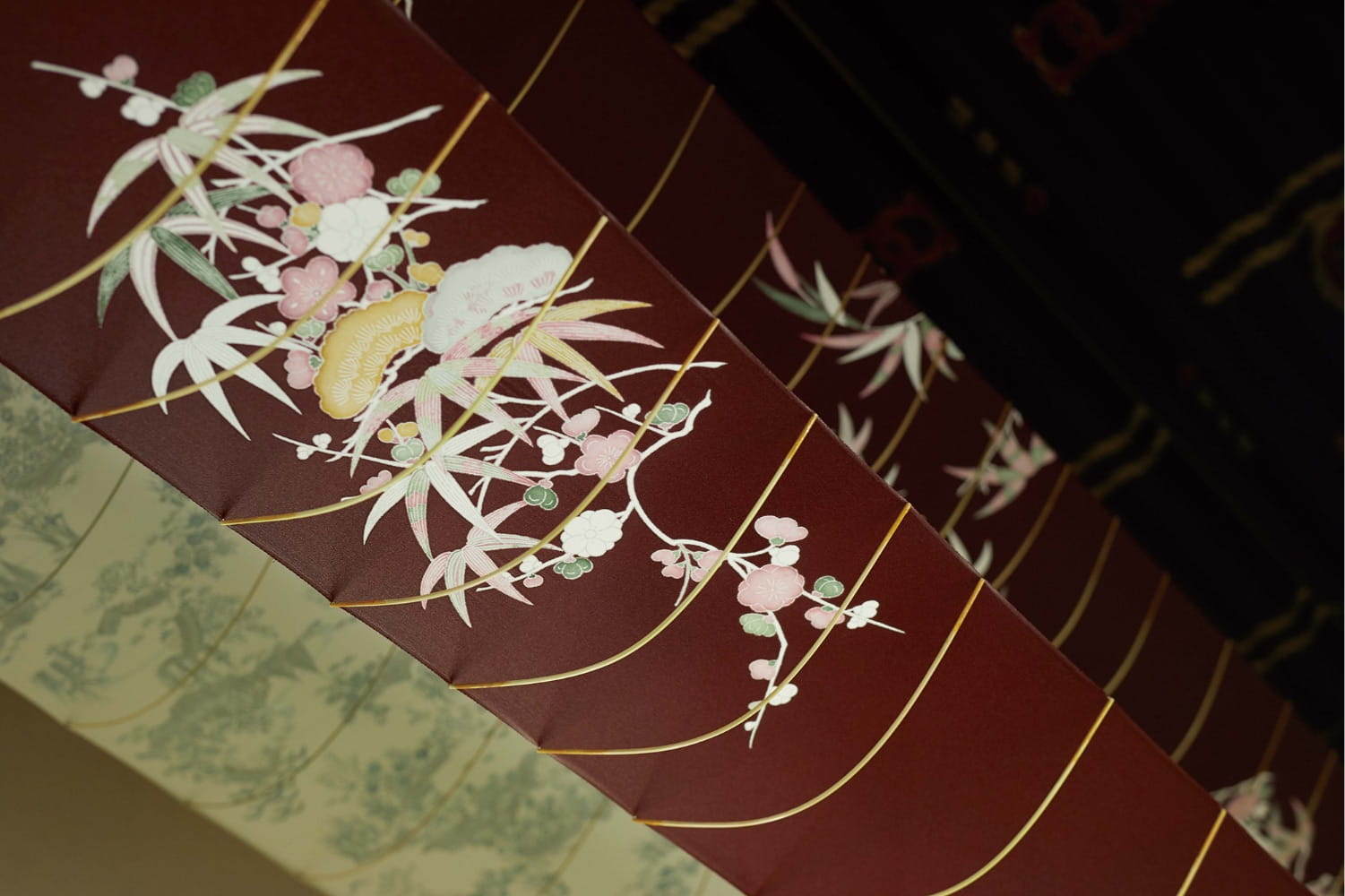
Now here's where the real history and collaborations come in. First up is the kimono Clé de Peau commissioned exclusively for the holiday collection. Fortunately for me (less work, haha!) the company did a fantastic job explaining the partnership and kimono-making process. "The kimono commissioned by Clé de Peau Beauté, created in collaboration with Tachibana, an embroidery and dyeing studio in Kyoto that plays a role in preserving kimono culture.1 Crafted using a valuable dyeing technique called Surigata-Yuzen, which uses dozens of stencils to dye different patterns, layering one color over another. Since Tachibana’s foundation in 1947, its colorful works have been captivating kimono fans. Founder Zenzo Sodesaki (born in 1911) learned the basics of making kimono at Chiso, a traditional Japanese textile producer and one of the oldest yuzen coloring companies in Kyoto. Current representative Yohei Kawai is the third generation, following Zenzo Sodesaki and second generation president, Kenichi Kawai." The red and pink colors were chosen specifically to match Clé de Peau's two holiday lipstick shades.
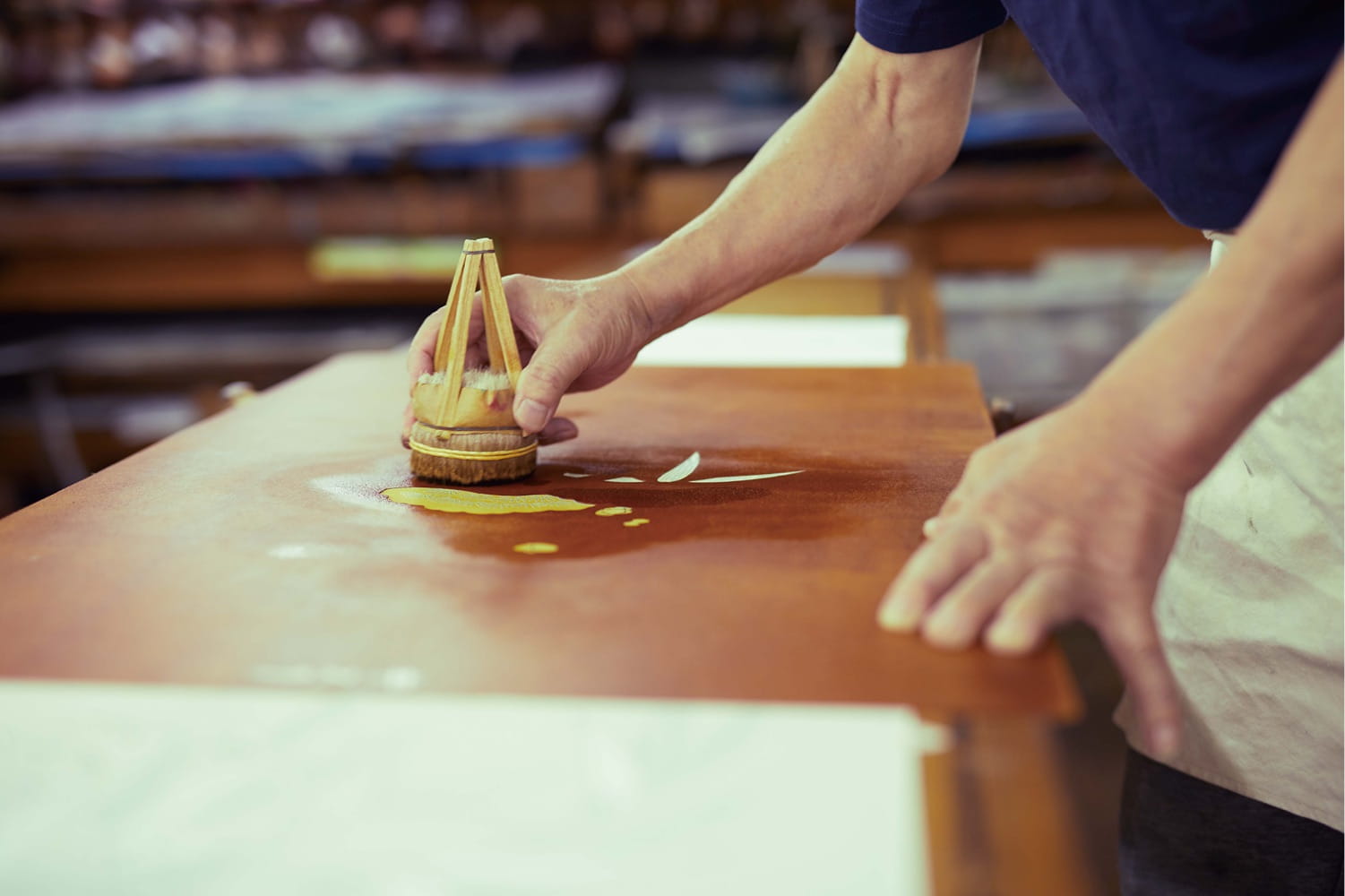
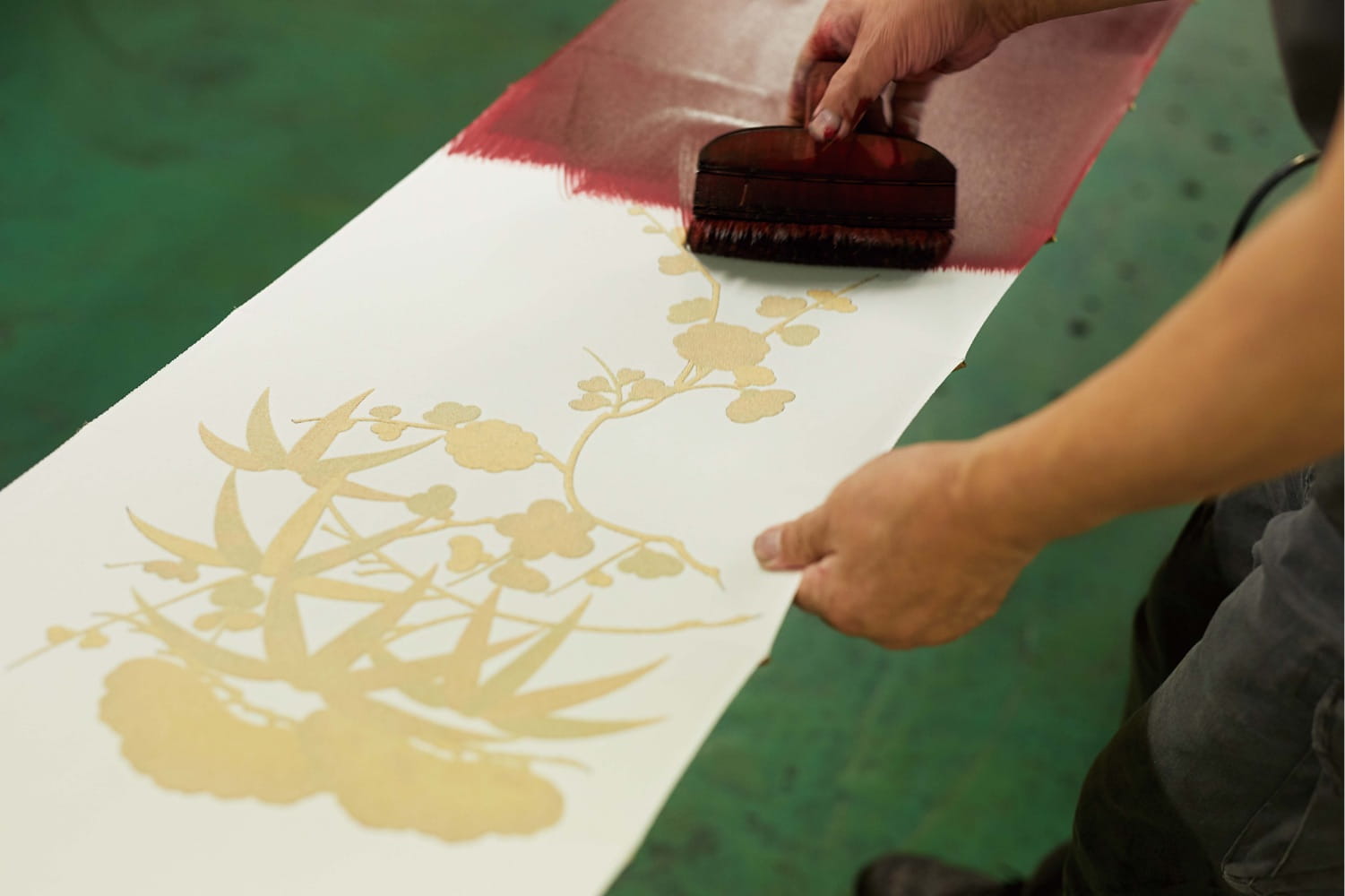
After the pattern is determined and sketched, it's time to stencil. The Clé de Peau kimono used a particular technique called Surigata-Yuzen. I'll let Clé de Peau describe the process in a nutshell. "The Surigata-Yuzen method uses dozens of stencils to dye patterns onto kimono silk, layering one color over another to produce a gradation. Every gradation is done by hand, adding another layer to the painstaking art of the kimono…For each color, dyeing is repeated in different tones, the layers achieving a complex and extraordinary beauty." A whopping 34 stencils were used for Clé de Peau's kimono.
Tachibana's bowtie website provided a little more insight into the process. "Dedicated professionals hand-carve patterns to create the stencils, which were at one time made simply of layered paper but are now mixed with resin to give them strength. Hoshi-awase, the positioning of the stencils, is one of the most important parts of the dyeing process. All of the stencils in a given pattern have small holes called hoshi. By aligning the hoshi of each stencil at the exact same place, dozens of stencils can be positioned on the fabric with great accuracy. Senshoku is the process of dyeing a pattern on fabric using brushes with colors. Various-sized brushes are used according to the size of a pattern. Once part of the fabric is dyed, a stencil is moved to the next place on the fabric. Stencils are accurately aligned using the hoshi holes. Pattern dyeing is followed by a process called noribuse, in which the whole pattern is covered with rice glue before dyeing with ground colors."
To be honest, I'm still confused as to how surigata-yuzen differs from other forms of yuzen techniques. This website seems to insinuate that surigata-yuzen is unique to Kyoto, therefore a subset of kyo-yuzen, but I'm really not sure.
Next, the entire kimono was hand-dyed with a brush via a process called Hikizome. Hikizome is used not just for kimonos but can be applied to all kinds of textiles – pillows, curtains, towels, etc. I believe this is true for yuzen as well, but once again I'm not certain.
The last step is to wait for the dye to dry in its own good time. According to Clé de Peau, "To make a kimono is to live by the laws of nature. So as not to alter the natural drying process, temperature condition is maintained the same throughout the year. The fate of the color finish is in the hands of nature, as the outcome is never the same." This aspect of the process fascinates me, especially for the Clé de Peau collection. The company wanted very specific colors that perfectly matched their two lipstick shades, so given that the drying is left to nature, how could they know for sure the color would turn out the way they wanted?
 (images from cledepeau-beaute.com)
(images from cledepeau-beaute.com)
Obviously it doesn't really matter, but it's interesting to consider that no one can predict the exact color. That makes the control freak in me rather anxious, but I can also appreciate the respect for nature. While I enjoyed reading about the kimono production process, I would have liked to see a little guide on how to fold and secure a kimono and how the obi fits in, as this aspect of the kimono was emphasized in the collection's packaging. Oh well.
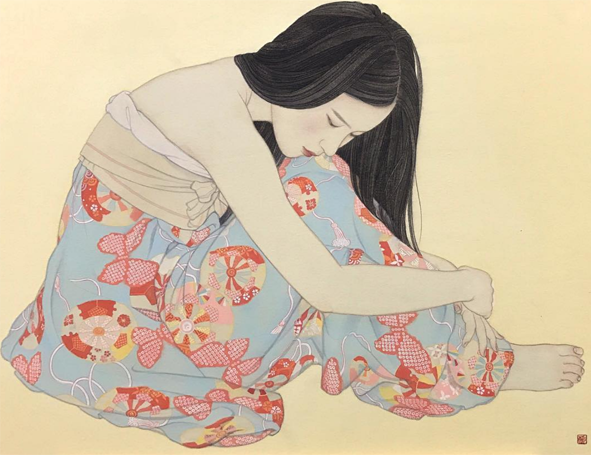
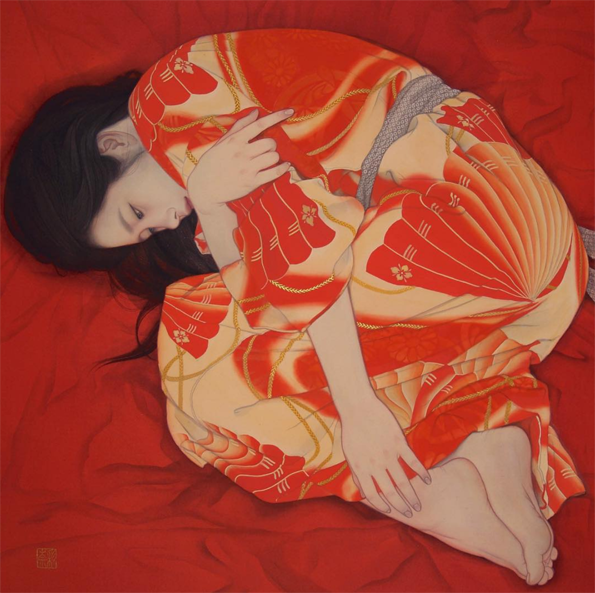
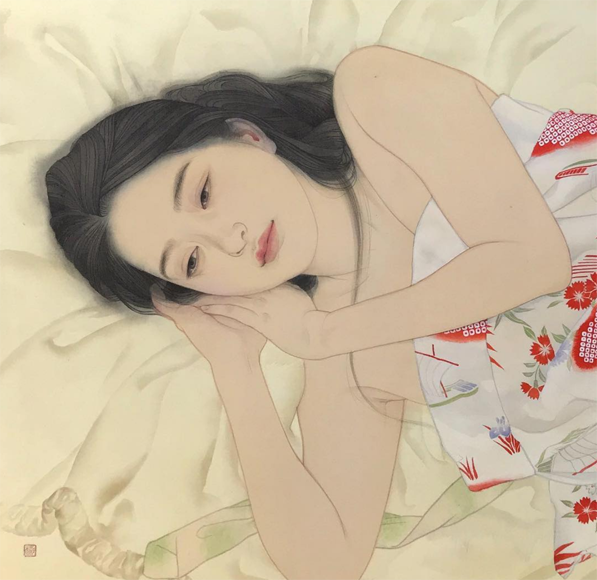
Now let's take a look at the amazing paintings by Ayana Otake, which graced the interiors of the packaging. Again, I didn't have to do much digging to get some information about Otake, for Clé de Peau also provided a brief bio. "Born in Saitama in 1981, Otake-san grew up surrounded by traditional culture and kimono. In 2007, she graduated in the Japanese Painting from the Department of Painting at Tokyo University of the Arts. She has produced works for galleries and department stores in Tokyo, and also practices bookbinding and package design." I would have liked to interview Otake to hear more about the Clé de Peau collaboration – I'm always curious to know how companies and artists find each other – but looking at Otake's other work as well as finding out a little about the tradition of bijin-ga will have to suffice.
Otake specializes in a modern version of bijin-ga. "Ga" means "picture" and "bijin" means "beautiful person", but is nearly always translated to "beautiful woman". Like kimonos, bijin-ga has an incredibly rich and long history. Part of me feels guilty for reducing it to a few paragraphs, but mostly I feel that since I'm not a Japanese art expert, I need to reign it in.
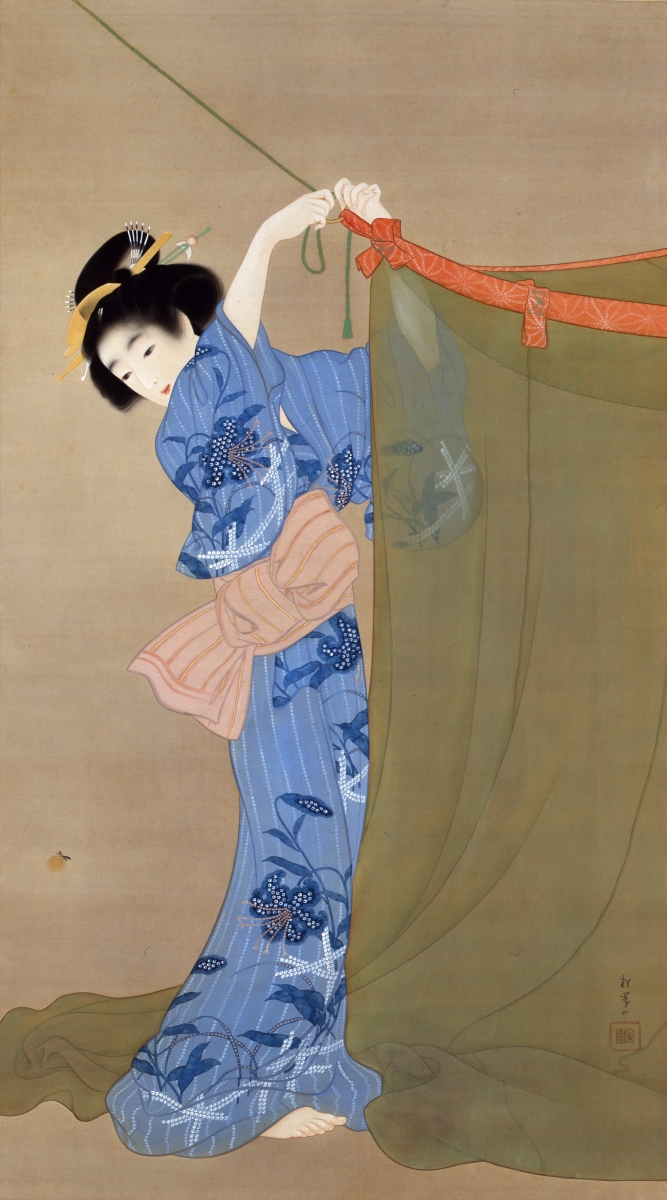
The genre of bijin-ga originated in the late 17th century and was popularized towards the end of the 18th century via ukiyo-e (woodblock prints). The women depicted at the outset were prostitutes, but over time bijin-ga expanded to include women from all walks of life. This website hosted by the Atsumi International Foundation explains the early origins of bijin-ga. "[W]ith the changes in society related to the rise of the merchant class, there was a new interest in depicting daily activities and pleasures of contemporary life. Popular entertainments were used for subject matter in paintings and then an interest developed in the beauty of personal appearance and form of women, including their clothing. Women of the brothels and pleasure quarters were predominately represented, and bijinga became a principal genre of the new *ukiyo-e 浮世絵. Single female figure portraits developed in the Kanbun 寛文 era (1661-73) with the Kanbun beauty *kanbun bijin 寛文美人. Typically, a yuujo 遊女 (courtesan or licensed prostitute) in a standing position was depicted in the bijinga of early ukiyo-e. Bijinga gradually broadened to include tea shop waitresses, the daughters and wives of tradesmen, etc. Nishikawa Sukenobu 西川祐信 (1671-1751) and Suzuki Harunobu 鈴木春信 (1725-70) produced pictures of women of various social classes, in addition to courtesans."2

(image from metmuseum.org)
In addition to portraying a variety of women, bijin-ga gradually expanded in the late 19th century to emphasize a woman's inner beauty as well as outer. "During the Meiji Era (1868-1912), portraits of beautiful women — which later became known as bijinga — evolved to focus on not only physical beauty, but also inner beauty. During this time, many artists excelled at bijinga, including Kiyokata Kaburaki (1878-1972), who was acclaimed for emotionally rich portraits; Shinsui Ito (1898-1972), who depicted real women rather than models; and Uemura Shoen (1875-1949), a female artist who brought a sense of dignity and refinement to the women she portrayed." As we'll see, I think Uemura Shoen's work in particular is a precursor to Otake's in that her paintings seek to express not just internal beauty but perhaps an inner monologue. The women in both artists' paintings appear very contemplative – I'd love to know what's going on in their heads. I'd also propose that both artists' perspectives are more feminist than they appear at first glance.

(image from japonica.info)
Anyway, the shin hanga ("new prints") art movement of the early 1900s cultivated further evolution of the bijin-ga genre. As the century progressed, the women portrayed became fully liberated from the earlier negative connotations, and the emphasis on capturing their internal beauty and positive traits became the primary attribute of modern bijin-ga. Otake's work continues the tradition of bijin-ga on a very basic level in that her paintings are of beautiful women; however, they have a thoroughly modern sensibility. Gone are the perfectly coiffed and made-up ladies of the old bijin-ga, as Otake shows women in a more natural, relaxed state – half-dressed with loose hair, lounging in bed or on the floor. There's a greater sense of intimacy and introspection in these scenes, as well as personal agency. These women don't seem to be waiting for anyone, they're simply enjoying some time alone.
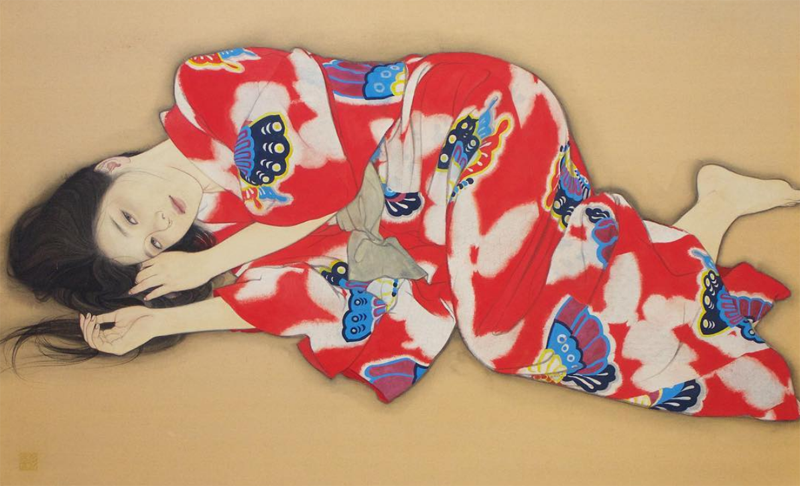 (images from @ayana_otake)
(images from @ayana_otake)
As far as I know Otake created original works for the Clé de Peau collection rather than recycling existing pieces. They tie into the collection not just through the inner beauty aspect but also by Otake's particular process, as her technique mimics one the methods used for kimono production. In the video below, she says: "When I'm not painting I look at greenery and try to be in touch with nature as much as possible…If it isn't sunny or a dry day, I can't work. So I look to the weather. Nothing beats natural drying. And authenticity is not about going against nature, but to live with nature, which I think is important." Otake notes that while sometimes she uses a dryer to speed up the drying time of her paintings, she usually "messes up". Her respect for nature and allowing it to complete her paintings serves as a parallel to letting the kimono dry naturally according to the weather, without any other intervention.
Overall, this is another winner from Clé de Peau. The intricacy of the packaging echoes the labor involved in the traditional kimono-making process, while the paintings serve as an updated version of a centuries-old artistic genre – it's a perfect marriage of old and new. I admired that for this collection, instead of doing a straight-up artist collaboration as in years past, (nothing wrong with those, of course!) they honored waning cultural traditions to raise awareness and educate people, a concept perhaps borrowed from Sulwhasoo's Shine Classic compacts. Finally, I loved all the details: the folding of the packaging, the fact that the paintings were on the inside to represent inner beauty, dyeing the kimono the same colors as the lipsticks, even the embossing on the boxes all came together to form a cohesive collection. I must congratulate the design team, as every last detail served a purpose. They were stunning, sure, but they also weren't superfluous – every single one contributed to the theme. I will say I'm scratching my head as to the whereabouts of Clé de Peau Creative Director Lucia Pieroni, as she doesn't seem to be as involved with this collection as in previous years, but the collection itself turned out beautifully.
What do you think of this collection? Which painting was your favorite?
1For further reading on the history and cultural meanings of the kimono I'd recommend Kimono: A Modern History.
2 This author points out that while they were euphemistically labeled as "courtesans", the prostitutes depicted in early bijin-ga had rather tragic lives. "Often the images were published with the prostitutes' names. Such prints were usually commissioned by high-ranking oiran as a kind of advertising posters. In today's print descriptions by ukiyo-e dealers or auction houses, the women shown on bijin prints are usually named 'courtesans'. The life for these 'courtesans' was not so beautiful. They were kept like slaves in these licensed quarters." Yikes.